EVPN Multihoming Split-Horizon Filters Not Functional
By: Anupam Murikurthy
Email: anupammurikurthy@gmail.com
READ THE FULL WRITE UP: VYOS EVPN MH BUG v2 - Google Docs
Goal:
This is a long write up for a bug, thanks for reading! My goal is to deploy a standards compliant active-active EVPN ESI LAG multihoming design using two VyOS/FRR leafs and multiple downstream L2 access switches connected via LACP. The EVPN control plane should allow me to:
-
Dual home multiple access switches to a pair of VyOS leafs for redundancy and active-active load balancing
-
Stretch L2 VLANs/VNIs across the fabric without loops
-
Ensure that the Designated Forwarder (DF) only forwards necessary BUM traffic toward the Ethernet Segment
-
Ensure that the non-DF drops all overlay originated BUM to prevent loops and MAC flapping
-
Maintain stable CAM tables on all downstream switches
-
Provide fast failover and consistent forwarding for hosts behind those downstream switches
Problem:
Split-horizon filtering is not working in FRR’s EVPN MH implementation.
Fabric Design: OSPF Underlay + eBGP EVPN + VXLAN
Tested On:
-
VyOS 1.5 Rolling + FRR 10.2.4 (vyos-2025.11.04-0019-rolling-generic-amd64)
-
Debian 13.1.0 + FRR 10.5 (manual configuration with systemd-networkd + FRR)
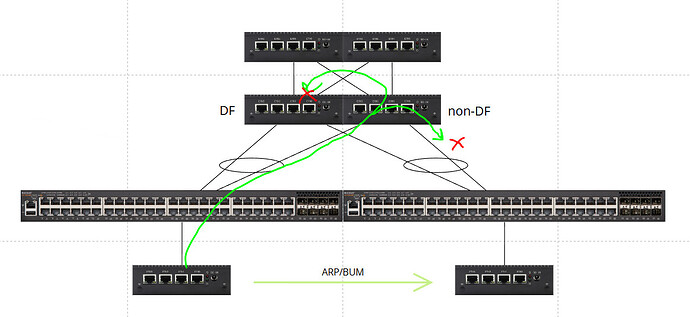
I’ve been testing EVPN ESI multihoming between two VyOS leaf switches and multiple downstream L2 switches using LACP. The EVPN control plane behavior appears correct (Type-1 AD, Type-2 MAC/IP, Type-3 IMET, Type-4 ES routes all install properly), however, ARP loops back into the ES and breaks multihoming standards whenever switching infrastructure is connected downstream in the data plane.
BUM traffic received on the non-DF leaf is being VXLAN encapsulated and sent to the DF, and then the DF leaf is flooding that BUM traffic back into the ES.
This should be impossible according to EVPN MH expectations across multiple vendors.
The result is:
-
MAC flapping on downstream switches
-
Blackholing of traffic / Packet loss
-
Downstream STP port blocking
-
Complete DoS conditions in networks with many MACs
Behavior Observed:
1. BUM Loop Behavior
-
A host connected to a downstream access switch generates BUM (ARP)
-
BUM arrives on LEAF2 (non-DF)
-
LEAF2 VXLAN encapsulates and forwards BUM to LEAF1 (DF)
-
LEAF1 (DF) decapsulates and floods the BUM back into the ES
-
Downstream switches now see the same host MAC arriving from the MH LAG and the host’s switch access port.
-
Switch CAM tables flap rapidly resulting in packet loss and instability
2. STP BPDUs Loop Behavior
-
A dual homed switch connected to VyOS leafs generates STP BPDUs
-
BPDUs arrive on LEAF2 (non-DF)
-
LEAF2 VXLAN encapsulates and forwards BPDUs to LEAF1 (DF)
-
LEAF1 (DF) decapsulates and floods the BPDUs back into the ES
-
The dual homed switch now sees STP it originated on the LAG
-
Switch blocks the LAG port or causes STP topology flapping
3. The Issue Scales With MAC Count and More Switches
-
In my small virtual lab with only a few MACs, Arista vEOS counted ~300 MAC moves/flaps within two minutes between the LAG and host access port
-
In my home network with many MACs and switches, this behavior caused a complete network wide denial of service, bringing the entire VLAN to a crawl
Request to Developers / How to Reproduce:
Please revisit the data plane implementation of split-horizon filtering for EVPN MH, particularly given that it is being advertised as a fully working capability.
The EVPN MH split-horizon issue is fully reproducible across multiple environments, operating systems, and FRR versions. Below is the setup required to reproduce the behavior, along with the exact VyOS 1.5 configs to trigger the MAC flapping and BUM looping.
I am more than willing to join a conference call to discuss this in depth with any interested developers.